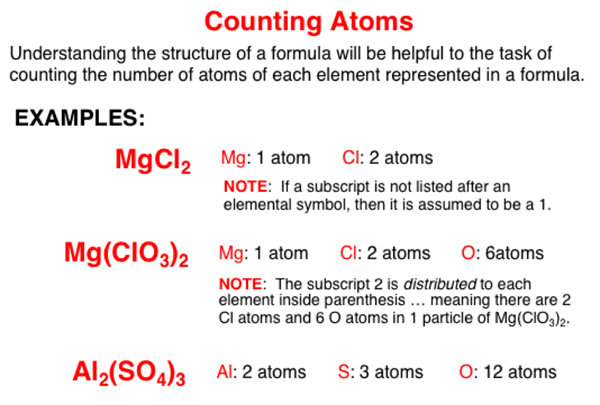
A compound consists of two or more elements. Elements are represnted by elemental symbols. A chemical formula for a compound identifies the elemental symbols of the elements in the compound and the number of atoms of each element. Subscripts listed immediately following an elemental symbol or after a group of symbols inside of parenthesis provides information about the number of atoms of each element.
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
Hold down the T key for 3 seconds to activate the audio accessibility mode, at which point you can click the K key to pause and resume audio. Useful for the Check Your Understanding and See Answers.
Molar Mass - helpApprentice
There are six groups of three questions (18 questions in all) in the first activity, titled Counting Atoms. Each question involves the same task. A chemical formula for a compound is given and the student must count the number of atoms of each element must be counted. An example question is shown below.
Version 1:
Counting the number of atoms of each element in a formula is a prerequisite skill to determining the molar mass. Count the number of atoms of each element in the formula Al2(SO4)3.