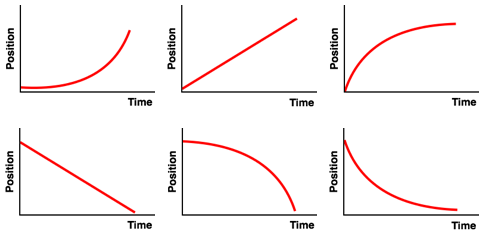
Identify what type of motion is being described by the velocity-time graph. This includes deciding whether the graph describes a constant speed, a speeding up, or a slowing down motion. It also includes deciding whether the graph describes an object moving with a positive or a negative velocity. Then determine how such features of an object's motion are represented on a position-time graph. Finally, identify the position-time graph that has these features.
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
Hold down the T key for 3 seconds to activate the audio accessibility mode, at which point you can click the K key to pause and resume audio. Useful for the Check Your Understanding and See Answers.
Match That Graph - help9
This question provides a velocity-time graph ....

... and asks the learner to identify the corresponding position-time graph: