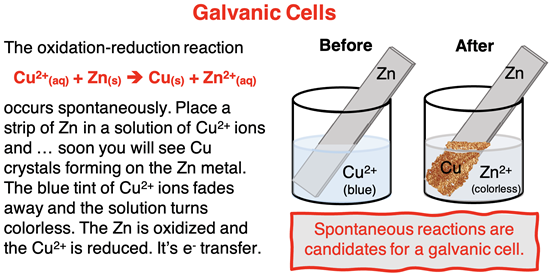
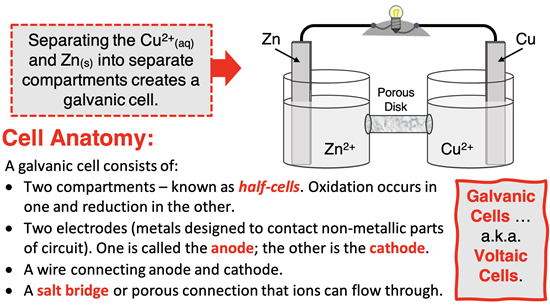
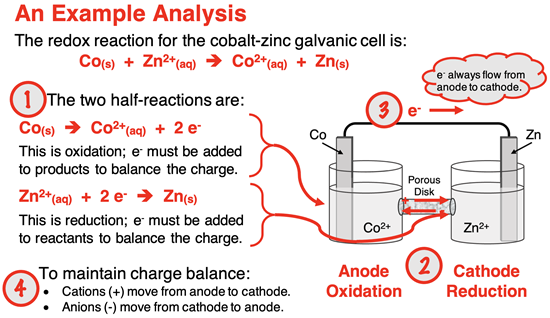
In a galvanic cell (or voltaic cell), the oxidation and reduction half-reactions occur in separate compartments known as half-cells. Electrons flow through a wire from the electrode where oxidation occurs (known as the anode) to the electrode where reduction occurs (known as the cathode). A salt bridge or other porous passageway between half-cells is used to facilitate ion flow and maintain electrical neutrality between the two half-cells.
Hold down the T key for 3 seconds to activate the audio accessibility mode, at which point you can click the K key to pause and resume audio. Useful for the Check Your Understanding and See Answers.
Galvanic Cells - help7
There are two questions in this Question Group. Here is one of those questions:
Question 1 of 2:
Question 13
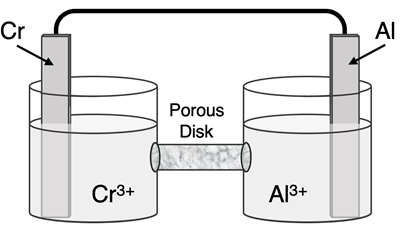
The redox reaction for this galvanic cell is:
Cr3+(aq) + Al(s) → Cr(s) + Al3+(aq)
Complete the galvanic cell diagram by identifying the half equations occurring in each half-cell, identifying the half-cell where oxidation occurs and the half-cell where reduction occurs, labeling the anode and the cathode, identifying the direction of electron flow in the wire, and identifying the direction of positive and negative ion flow through the porous membrane.