Mission LC5 Color Subtraction

Three colored spotlights - red, green and blue - with equal intensities are used to illuminate a shirt with different colors of light. If a shirt which appears red under white light is illuminated with cyan light, then the shirt will absorb the ____ light and appear as _____.
(Note: the actual colors listed are generated at random and may vary from the above.)

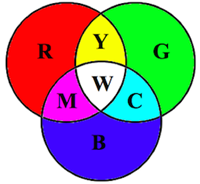 Many students of physics have seen a diagram similar to the one shown at the right. The diagram depicts three circles colored with the primary colors of light - red, green and blue. The primary colored circles overlap to produce other colors of light - known as the secondary colors of light: cyan, magenta and yellow. Complementary pairs of light colors are those colors that are exactly opposite each other on the diagram: red and cyan, magenta and green, and blue and yellow.
Many students of physics have seen a diagram similar to the one shown at the right. The diagram depicts three circles colored with the primary colors of light - red, green and blue. The primary colored circles overlap to produce other colors of light - known as the secondary colors of light: cyan, magenta and yellow. Complementary pairs of light colors are those colors that are exactly opposite each other on the diagram: red and cyan, magenta and green, and blue and yellow.
An object that is observed to be a specific color when illuminated with white light has absorbed the complementary color of the observed color. White light or R+ G + B was incident on the object. One or more of the components of white light were absorbed or subtracted and the remaining light colors were reflected to the observer's eye.

The color a shirt appears is related to the wavelengths (colors) of light that it reflects. A shirt can appear red when normal white light shines on it because it reflects red light and absorbs blue and green light. (See the Dig that Diagram and Know the Law section.) But if the light that shines upon it is changed, there may be no red to reflect and its appearance could change.
From the appearance of the shirt in the presence of white light, we can infer what the shirt can do to each of the three primary colors of light. We know that the shirt can absorb blue and green light (when blue and green shine on it) and can reflect red light (when red shines on it). Now, let's shine cyan light on it. Cyan light is a combination of green and blue light (see Dig that Diagram section). The shirt is capable of absorbing the green and blue light so it becomes absorbed. What gets reflected? Nothing. Green and blue light were the only primary colors of light shining on it. Green and blue light are absorbed, nothing is reflected and the shirt appears black.
