Refraction and Lenses Review
Part A: Multiple Choice
1. The best definition of refraction is ____.
|
a. passing through a boundary
|
b. bouncing off a boundary
|
|
c. changing speed at a boundary
|
d. changing direction when crossing a boundary
|
2. If carbon tetrachloride has an index of refraction of 1.461, what is the speed of light through this liquid? (c = 3 x 108 m/s)
|
a. 4.38 x 108 m/s
|
b. 2.05 x 108 m/s
|
c. 4.461 x 108 m/s
|
d. 1.461 x 108 m/s
|
3. A ray of light in air is incident on an air-to-glass boundary at an angle of 30. degrees with the normal. If the index of refraction of the glass is 1.65, what is the angle of the refracted ray within the glass with respect to the normal?
|
a. 56 degrees
|
b. 46 degrees
|
c. 30. degrees
|
d. 18 degrees
|
4. If the critical angle for internal reflection inside a certain transparent material is found to be 48.0 degrees, what is the index of refraction of the material? (Air is outside the material).
|
a. 1.35
|
b. 1.48
|
c. 1.49
|
d. 0.743
|
5. Carbon disulfide (n = 1.63) is poured into a container made of crown glass (n = 1.52). What is the critical angle for internal reflection of a ray in the liquid when it is incident on the liquid-to-glass surface?
|
a. 89.0 degrees
|
b. 68.8 degrees
|
c. 21.2 degrees
|
d. 4.0 degrees
|
6. Carbon tetrachloride (n = 1.46) is poured into a container made of crown glass (n = 1.52). If the light ray in glass incident on the glass-to-liquid boundary makes an angle of 30 degrees with the normal, what is the angle of the corresponding refracted ray with respect to the normal?
|
a. 55.5 degrees
|
b. 29.4 degrees
|
c. 31.4 degrees
|
d. 19.2 degrees
|
7. A light ray in air is incident on an air to glass boundary at an angle of 45.0 degrees and is refracted in the glass of 30.0 degrees with the normal. What is the index of refraction of the glass?
|
a. 2.13
|
b. 1.74
|
c. 1.23
|
d. 1.41
|
8. A beam of light in air is incident at an angle of 35 degrees to the surface of a rectangular block of clear plastic (n = 1.5). The light beam first passes through the block and reemerges from the opposite side into air at what angle to the normal to that surface?
|
a. 42 degrees
|
b. 23 degrees
|
c. 35 degrees
|
d. 59 degrees
|
9. A light ray in air enters and passes through a block of glass. What can be stated with regard to its speed after it emerges from the block?
|
a. speed is less than when in glass
|
b. speed is less than before it entered glass
|
|
c. speed is same as that in glass
|
d. speed is same as that before it entered glass
|
10. Which of the following describes what will happen to a light ray incident on an air-to-glass boundary?
|
a. total reflection
|
b. total transmission
|
|
c. partial reflection, partial transmission
|
d. partial reflection, total transmission
|
11. Which of the following describes what will happen to a light ray incident on an air-to-glass boundary at an angle of incidence less than the critical angle?
|
a. total reflection
|
b. total transmission
|
|
c. partial reflection, partial transmission
|
d. partial reflection, total transmission
|
12. Which of the following describes what will happen to a light ray incident on an glass-to-air boundary at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle?
|
a. total reflection
|
b. total transmission
|
|
c. partial reflection, partial transmission
|
d. partial reflection, total transmission
|
13. What is the angle of incidence on an air-to-glass boundary if the angle of refraction in the glass (n = 1.52) is 25 degrees?
|
a. 16 degrees
|
b. 25 degrees
|
c. 40 degrees
|
d. 43 degrees
|
14. A ray of white light, incident upon a glass prism, is dispersed into its various color components. Which one of the following colors experiences the greatest amount of refraction?
|
a. orange
|
b. violet
|
c. red
|
d. green
|
15. When light from air hits a smooth piece of glass (n = 1.5) with the ray perpendicular to the glass surface, which of the following will occur?
|
a. reflection and transmission at an angle of 0 degrees
|
b. dispersion
|
|
c. refraction at an angle of 41.8 degrees
|
d. all of the above will occur
|
16. If total internal reflection occurs at a glass-air surface, then _____.
- no light is refracted
- no light is reflected
- light is leaving the air and hitting the glass with an incident angle greater than the critical angle
- light is leaving the air and hitting the glass with an incident angle less than the critical angle
17. When light from air hits a smooth piece of glass with the ray perpendicular to the glass surface, the part of the light passing into the glass _____.
|
a. will not change its speed
|
b. will not change its direction
|
|
c. will not change its wavelength
|
d. will not change its intensity
|
For Questions #18 - #20, consider the diagram below.
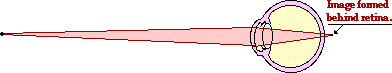
18. This person suffers from the problem of ____.
|
a. nearsightedness
|
b. farsightedness
|
c. cataracts
|
d. delusions
|
19. This problem could most easily be corrected by the use of a(n) ____.
|
a. converging lens
|
b. diverging lens
|
c. achromatic lens
|
d. good night's sleep
|
20. If the image was formed in front of the retina rather than behind the retina, then the person would need to correct the vision problem by using a
|
a. converging lens
|
b. diverging lens
|
c. achromatic lens
|
d. alarm clock
|
21. Dispersion occurs when _____.
- some materials bend light more than other materials
- a material slows down some colors more than others
- a material changes some colors more than others
- light has different speeds in different materials
22. A 3.0 cm tall object is placed along the principal axis of a thin converging lens of 30.0 cm focal length. If the object distance is 40.0 cm, which of the following best describes the image distance and height, respectively?
|
a. 17.3 cm and 7.0 cm
|
b. 120. cm and -9.0 cm
|
c. 17.3 cm and 1.3 cm
|
d. 120. cm and -1.0 cm
|
23. Which of the following best describes the image for a thin converging lens that forms whenever the object is at a distance less than one focal length from the lens?
|
a. inverted, enlarged and real
|
b. upright, enlarged and virtual
|
|
c. upright, reduced and virtual
|
d. inverted, reduced and real
|
24. Which of the following best describes the image for a thin diverging lens that forms whenever the magnitude of the object distance is less than that of the lens' focal length?
|
a. inverted, enlarged and real
|
b. upright, enlarged and virtual
|
|
c. upright, reduced and virtual
|
d. inverted, reduced and real
|
25. An object is placed at a distance of 30.0 cm from a thin converging lens along its axis. The lens has a focal length of 10.0 cm. What are the values of the image distance and magnification (respectively)?
|
a. 60.0 cm and 2.00
|
b. 15.0 cm and 2.00
|
c. 60.0 cm and -0.500
|
d. 15.0 cm and -0.500
|
26. An object is placed at a distance of 6.0 cm from a thin converging lens along its axis. The lens has a focal length of 9.0 cm. What are the values, respectively, of the image distance and magnification?
|
a. -18 cm and 3.0
|
b. 18 cm and 3.0
|
c. 3.0 cm and -0.50
|
d. -18 cm and -3.0
|
27. An object is placed at a distance of 30.0 cm from a thin converging lens along the axis. If a real image forms at a distance of 10.0 cm from the lens, what is the focal length of the lens?
|
a. 30.0 cm
|
b. 15.0 cm
|
c. 10.0 cm
|
d. 7.50 cm
|
28. An object is placed at a distance of 40.0 cm from a thin lens along the axis. If a virtual image forms at a distance of 50.0 cm from the lens, on the same side as the object, what is the focal length of the lens?
|
a. 22.2 cm
|
b. 45.0 cm
|
c. 90.0 cm
|
d. 200. cm
|
Part B: Multiple-Multiple Choice
29. Which of the following statements are true of converging lenses? Identify all that apply.
- Converging lenses are thicker at the center than they are at the edges.
- If the bottom half of a converging lens is covered, then the top half of the image will not be visible.
- Converging lenses only produce real images.
- Converging lenses can produce images which are both magnified and reduced in size.
- Converging lenses only produce inverted images.
- Converging lenses have a + focal length.
- The images formed by a converging lens can be located on either side of the lens relative to the object.
30. Which of the following statements are true of diverging lenses? Identify all that apply.
- Diverging lenses are thicker at the center than they are at the edges.
- If the bottom half of a diverging lens is covered, then the bottom half of the image will not be visible.
- Diverging lenses only produce virtual images.
- Diverging lenses can produce images which are both magnified and reduced in size.
- Diverging lenses only produce upright images.
- Diverging lenses have a - focal length.
- The images formed by a diverging lens can be located on either side of the lens relative to the object.
31. Which of the following statements are true of real images? Identify all that apply.
- Real images are inverted.
- Real images as formed by lenses are located on the opposite side of the lens from the object.
- Real images are magnified in size.
- Real images are only formed by converging lenses, never by diverging lenses.
- An image of a real object is formed; the image distance (s' or di) for real images is a + value.
- An image of a real object is formed; the image height (h' or hi) for real images is a + value.
- Real images have a - magnification value.
32. Which of the following statements are true of virtual images? Identify all that apply.
- Virtual images are always upright.
- Virtual images as formed by lenses are always located on the same side of the lens as the object.
- Virtual images are only formed by diverging lenses, never by converging lenses.
- Virtual images are always smaller than the object.
- An image of a real object is formed; the image distance (s' or di) for virtual images is a - value.
- An image of a real object is formed; the image height (h' or hi) for virtual images is a - value.
- Virtual images have a - magnification value.
33. Several characteristics of images are described below. Determine whether these images are real or virtual and whether they are formed by converging, diverging lenses or either type. (In all cases, assume that the object is an upright and real object.)
- Image is upright and magnified.
- Image if upright and reduced in size.
- Image is inverted and magnified.
- Image has a negative s' (di) value.
- Image has a negative h' (hi) value.
- Image has a positive h' (hi) value and a magnification value greater than 1.
34. Which of the following statements are true of total internal reflection (TIR)? Include all that apply.
- TIR can only occur when light approaches a boundary and is incident within the most dense media.
- TIR can only occur when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
- TIR causes a portion of the light to refract along the boundary and the rest to be reflected.
- When TIR occurs, the reflected light follows the law of reflection.
- If TIR occurs at the boundary of water and air, then the light must be within water and heading towards the boundary with air.
- If TIR occurs at the boundary of glass and air, then it is possible that the light is traveling within air and heading towards the glass.
Part C: Diagramming and Analysis
|
35. The diagram below shows four incident rays traveling through water (n = 1.33) and approaching the boundary with air (n=1.00). For each incident ray, draw the corresponding reflected ray; then calculate the angle of refraction and draw the corresponding refracted ray. Label or color code your reflected and refracted rays to distinguish them from each other and to match them to the incident ray.
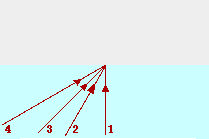
|
Ray
|
Angle of
incidence
|
Angle of
reflection
|
Angle of
refraction
|
|
1
|
0.0 deg.
|
_______
|
_______
|
|
2
|
30.0 deg.
|
_______
|
_______
|
|
3
|
45.0 deg.
|
_______
|
_______
|
|
4
|
60.0 deg.
|
_______
|
_______
|
36. In the diagrams below, construct refracted rays to indicate the direction which the light rays bend upon crossing the boundary.
If light travels faster in medium 1 than in medium 2, then upon entering medium 2, the light will bend towards from the normal.
|
If the index of refraction of medium 1 is greater than medium 2, then upon entering medium 2, the light will bend away from the normal.
|
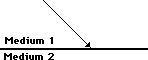
|

|
37. Use Snell's law, a protractor and a straight-edge to trace the path of light through the following objects.
38. Construct ray diagrams to show where the images of the following objects are located. Draw in the complete image (approximated by an arrow) and describe its characteristics (real or virtual, enlarged or reduced in size, inverted or upright).
|
|
|
Real or Virtual?
|
Magnified or Reduced?
|
Upright or Inverted?
|
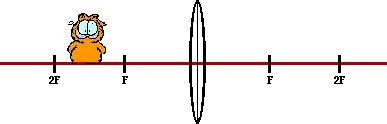
|
|
Real or Virtual?
|
Magnified or Reduced?
|
Upright or Inverted?
|

|
|
Real or Virtual?
|
Magnified or Reduced?
|
Upright or Inverted?
|
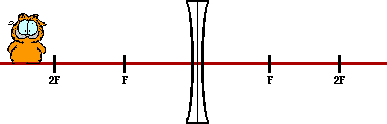
|
|
Real or Virtual?
|
Magnified or Reduced?
|
Upright or Inverted?
|
Part D: Problem-Solving
39. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.00 x 108 m/s. Determine the speed of light through the following materials.
- air (n=1.00)
- ethanol (n=1.36)
- crown glass (n=1.52)
- zircon (n=1.91)
- diamond (n=2.42)
 40. Bruno is standing upon the edge of the water with his high-powered laser gun, waiting to zap the next visible fish with a burst of laser light. Frieda deFish, located a distance of 2.17 m out from shore, hopes to hide from view by ducking behind a small lily pad. If Bruno's laser is located 0.850-m above the ground and the lily pad is 1.39 m from shore, then to what depth below the water must Frieda descend in order to be hidden from view? (Given: nwater = 1.33)
40. Bruno is standing upon the edge of the water with his high-powered laser gun, waiting to zap the next visible fish with a burst of laser light. Frieda deFish, located a distance of 2.17 m out from shore, hopes to hide from view by ducking behind a small lily pad. If Bruno's laser is located 0.850-m above the ground and the lily pad is 1.39 m from shore, then to what depth below the water must Frieda descend in order to be hidden from view? (Given: nwater = 1.33)
 41. Frieda deFish, disturbed at Bruno's militance, pulls out a laser of her own. She temporarily ducks out from her cover and aims it upwards at an angle of 26.5-degrees at Bruno's nose. If Bruno's nose is 1.34-m above the water's edge and if Frieda is a distance of 0.91 m below the water's surface, then how far out from shore must Frieda be to have a direct hit?
41. Frieda deFish, disturbed at Bruno's militance, pulls out a laser of her own. She temporarily ducks out from her cover and aims it upwards at an angle of 26.5-degrees at Bruno's nose. If Bruno's nose is 1.34-m above the water's edge and if Frieda is a distance of 0.91 m below the water's surface, then how far out from shore must Frieda be to have a direct hit?
42. Determine the critical angle for the following boundaries:
- air - crown glass (n=1.52)
- air - diamond (n=2.42)
- crown glass (n=1.52) - diamond (n=2.42)
- air - Lucite (n=1.40)
- air and a material through which light travels at a speed of 2.10 x 108 m/s
43. A lens produces an upright image of an object. The image is reduced in size by a factor of 3.00 when the object is a distance of 16.9 cm from the lens. Determine the focal length.
44. A thin lens has a focal point located 19.7 cm from the lens surface. When the object is placed at a specific location, the virtual image it produces is one-fourth the size of the object. Determine the object distance. (Careful of your sign on f.)
45. A thin lens has a focal point located 16.8 cm from the lens surface. Determine the object location which would produce an inverted image which is exactly five times larger than the object.
46. A thin lens has a focal point located 16.8 cm from the lens surface. Determine the object location which would produce an upright image which is exactly five times larger than the object.
Navigate to:
Review Session Home - Topic Listing
Refraction and Lenses - Home || Printable Version || Questions with Links
Answers to Questions: All || #1-#20 || #21-#34 || #35-#46
You Might Also Like ...
Users of The Review Session are often looking for learning resources that provide them with practice and review opportunities that include built-in feedback and instruction. If that is what you're looking for, then you might also like the following:
- The Calculator Pad
The Calculator Pad includes physics word problems organized by topic. Each problem is accompanied by a pop-up answer and an audio file that explains the details of how to approach and solve the problem. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to improve their problem-solving skills.
Visit: The Calculator Pad Home | Calculator Pad - Refraction and Lenses
- Minds On Physics the App Series
Minds On Physics the App ("MOP the App") is a series of interactive questioning modules for the student that is serious about improving their conceptual understanding of physics. Each module of the series covers a different topic and is further broken down into sub-topics. A "MOP experience" will provide a learner with challenging questions, feedback, and question-specific help in the context of a game-like environment. It is available for phones, tablets, Chromebooks, and Macintosh computers. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to refine their conceptual reasoning abilities. Part 6 of the series includes topics in Refraction and Lenses.
Visit: MOP the App Home || MOP the App - Part 6