A force that is applied to a seesaw along a line that does not extend through the axis of rotation (i.e., the fulcrum) will cause the seesaw to rotate. The direction of rotation depends on the direction of the force. And the sign on the resulting torque is associated with the direction of rotation of the seesaw.
Torque - Questions 9 Help
There are four similar versions of this question. Here is one of the versions:
Version 1:
A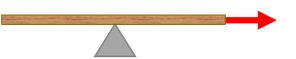 force is applied to a see-saw as shown. Which one of the following statements regarding the resulting torque and rotation is true?
force is applied to a see-saw as shown. Which one of the following statements regarding the resulting torque and rotation is true?Because of the direction of this force, there is no torque and no rotation.
The torque will cause a clockwise rotation; it's sign would be positive.
The torque will cause a clockwise rotation; it's sign would be negative.
The torque will cause a counter-clockwise rotation; it's sign would be positive.
The torque will cause a counter-clockwise rotation; it's sign would be negative.
Try these links to The Physics Classroom Tutorial for more help with understanding the concept of torque and rotation:
Sorry. We hope to add resources in the future.