Work and Energy Review
Navigate to:
Review Session Home - Topic Listing
Work and Energy - Home || Printable Version || Questions with Links
Answers to Questions: All || #1-10 || #11-25 || #26-36 || #37-45
Part D: Complex Analysis and Problem-Solving
37. A 21.3-kg child positions himself on an inner-tube which is suspended by a 7.28-m long rope attached to a strong tree limb. The child and tube is drawn back until it makes a 17.4-degree angle with the vertical. The child is released and allowed to swing to and from. Assuming negligible friction, determine the child's speed at his lowest point in the trajectory. PSYW
|
Answer: 2.56 m/s
This is an example of energy transformation from potential energy at the highest point (the point of release) to kinetic energy at the lowest position. Since gravity is the only force doing work (tension acts perpendicular to the displacement so it does not do work), the total mechanical energy is conserved. So the energy conservation equation will be used.
KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf
Since the child starts from rest, the KEi term can be canceled. And if we assign the lowest position as the zero-level, then the PEf term can be canceled from the equation. The equation can be rewritten as
PEi = KEf
By substituting in expressions for kinetic and potential energy, the equation becomes
m • g • hi = 0.5 • m • vf2
The mass cancels from each side of the equation, and algebra can be used to manipulate the equation to solve for vf.
vf = SQRT( 2 • g • hi )
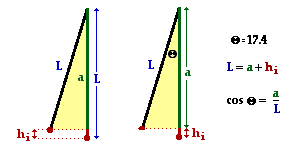 The crux of the problem becomes determining the initial height of the child. The length of the cables and the angle to which it is drawn back will be essential information in determining the initial height. The diagram at the right depicts the physical situation. The length of the cable is the hypotenuse of a triangle; the length of the side adjacent to the 17.4-degree angle can be determined using the cosine function. This adjacent side (a) is shorter than the length of the cable by an amount equal to the initial height (hi). The work is shown below: The crux of the problem becomes determining the initial height of the child. The length of the cables and the angle to which it is drawn back will be essential information in determining the initial height. The diagram at the right depicts the physical situation. The length of the cable is the hypotenuse of a triangle; the length of the side adjacent to the 17.4-degree angle can be determined using the cosine function. This adjacent side (a) is shorter than the length of the cable by an amount equal to the initial height (hi). The work is shown below:
cos(17.4 deg) = a/L
a = L • cos(17.4 deg) = 6.95 m
hi = L - a = 7.28 m - 6.95 mm = 0.333 m
Once hi is found, it can be substituted into the above equation to solve for the final velocity:
vf = SQRT ( 2 • 9.8 m/s/s • 0.33 m) = SQRT(6.53 m/s) = 2.56 m/s
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
38. A baseball player catches a 163-gram baseball which is moving horizontally at a speed of 39.8 m/s. Determine the force which she must apply to the baseball if her mitt recoils a horizontal distance of 25.1 cm. PSYW
|
Answer: 514 N
This is an example of work being done by a non-conservative force (the applied force of the mitt) upon a baseball in order to change its kinetic energy. So
Wnc = Change in KE
The change in kinetic energy can be computed by subtracting the initial value (0.5 • m • vi2) from the final value (0 J) .
Change in KE = KEf - KEi = 0 J - 0.5 • (0.163 kg) • (39.8 m/s)2 = -129 J
The force can be determined by setting this value equal to the work and using the expression for work into the equation:
Wnc = -129 J
F • d • cos(theta) = -129 J
F • (0.251 m) • cos(180 deg) = -129 J
F = 514 N
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
39. A 62.9-kg downhill skier is moving with a speed of 12.9 m/s as he starts his descent from a level plateau at 123-m height to the ground below. The slope has an angle of 14.1 degrees and a coefficient of friction of 0.121. The skier coasts the entire descent without using his poles; upon reaching the bottom he continues to coast to a stop; the coefficient of friction along the level surface is 0.623. How far will he coast along the level area at the bottom of the slope? PSYW
|
Answer: 116 m
During the entire descent down the hill, gravity is doing work on the skier and friction is doing negative work on the skier. Friction is a non-conservative force and will alter the total mechanical energy of the skier. The equation to be used is
KEi + PEi + Wnc = KEf + PEf
If we designate the level area at the bottom of the slope as the zero level of potential energy, then PEf is 0 J. Since the skier eventually stops (due to the effect of friction along the level area), the KEf is 0 J. So the above equation becomes
KEi + PEi + Wnc = 0
The Wnc term has two parts; there is friction doing along the inclined plane and friction doing work along the level surface. Since these two sections of the motion have different normal forces and friction coefficients (and therefore friction forces), they will have to be treated separately. The graphic below depicts the free-body diagrams and the means by which the friction force can be determined.
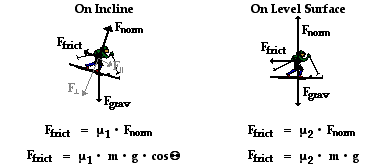
By substituting values of mu and mass and g and theta into the above equations, one finds that the friction values are
|
On Incline
Ffrict = 72.3 N
|
On Level Surface
Ffrict = 384 N
|
These forces act upon the skier over different distances. In the case of the inclined plane, the distance (d) can be computed from the given incline angle and the initial height. The relationship is depicted in the diagram below. The sine function is used to relate the angle to the initial height and the distance along the incline. In the case of the level surface, the distance is the unknown quantity (x) which this problem calls for.
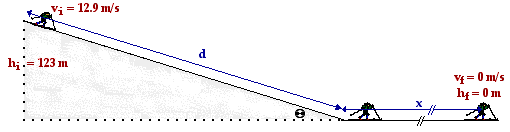
The distance d along the incline is
d = hi / sin(theta) = 123 m / sin(14.1 deg) = 505 m
Now substitutions can be made into the work-energy equation and algebraic manipulation can be performed to solve for x:
KEi + PEi + Wnc = 0
KEi + PEi + Wincline + Wlevel = 0
0.5•(62.9 kg)•(12.9 m/s)2 + (62.9 kg)•(9.8 m/s)•(123 m) + (72.3 N)•(505 m)•cos(180 deg) + (384 N)•(x)•cos(180 deg) = 0 J
5233 J + 75820 J - 36512 J - 384 x = 0 J
44541 J = 384 x
116 m = x
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
40. A 29.1-kg sledder is traveling along a level area with a speed of 8.96 m/s when she approaches a gentle incline which makes an angle of 12.5 degrees with the horizontal. If the coefficient of friction between the sled and the incline is 0.109, then what will be her speed at the bottom of the inclined plane, located 8.21 m above the top of the incline. PSYW
|
Answer: 12.7 m/s
This problem is similar to the above. During the entire descent down the hill, gravity is doing work on the sledder and friction is doing negative work on the sledder. Friction is a non-conservative force and will alter the total mechanical energy of the sledder. The equation to be used is
KEi + PEi + Wnc = KEf + PEf
If we designate the level area at the bottom of the slope as the zero level of potential energy, then PEf is 0 J. So the above equation becomes
KEi + PEi + Wnc = KEf
0.5•m•vi2 + m•g•hi + F•d•cos(theta) = 0.5•m•vf2
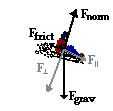 The Wnc term results from friction acting upon the sledder. The force of friction is given by the equation Ffrict = mu • Fnorm. For inclined planes the normal force is equal to the perpendicular component of the weight vector (see diagram at the right). This component is equal to the expression m•g•cos(theta) where theta is the incline angle (12.5 degrees). So the force of friction is The Wnc term results from friction acting upon the sledder. The force of friction is given by the equation Ffrict = mu • Fnorm. For inclined planes the normal force is equal to the perpendicular component of the weight vector (see diagram at the right). This component is equal to the expression m•g•cos(theta) where theta is the incline angle (12.5 degrees). So the force of friction is
Ffrict = mu•m•g•cos(theta)
Ffrict = (0.109)•(29.1 kg)•(9.8 m/s/s)•cos(12.5 deg) = 30.3 N
The work done by the friction force occurs over the entire length of the inclined plane. This distance is related to the initial height and the incline angle by the equation sin(theta) = hi/d (see diagram below). Using 12.5 degrees for theta and 8.21 m for the initial height, the distance along the incline (d) can be determined to be 37.9 m. The diagram below depicts the physical situation.
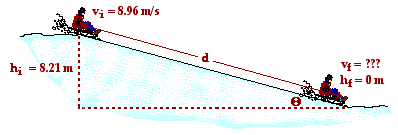
Now substitutions can be made into the earlier stated equation and algebra manipulations can be performed to determine the final speed. The work is shown below.
0.5•m•vi2 + m•g•hi + F•d•cos(theta) = 0.5•m•vf2
0.5•(29.1 kg)•(8.96 m/s)2 + (29.1 kg)•(9.8 m/s/s)•(8.21 m) + (30.3 N)(37.9 m)•cos(180 deg)= 0.5•(29.1 kg)•vf2
1168 J + 2341 J - 1148 J = (14.6 kg)•vf2
162.3 m2/s2 = vf2
vf = SQRT(162.3 m2/s2) = 12.7 m/s
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
41. A 221-gram ball is thrown at an angle of 17.9 degrees and a speed of 36.7 m/s from the top of a 39.8-m high cliff. Determine the impact speed of the ball when it strikes the ground. Assume negligible air resistance. PSYW
|
Answer: 46.1 m/s
 Here is a situation in which the only force doing work -gravity - is a conservative force; so the total mechanical energy of the system is conserved. The conservation of energy equation can be used. Here is a situation in which the only force doing work -gravity - is a conservative force; so the total mechanical energy of the system is conserved. The conservation of energy equation can be used.
KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf
If we assign the ground below the cliff to be the zero-level of potential energy, then the PEf term can be canceled from the equation.
KEi + PEi = KEf
Expressions for kinetic and potential energy can be substituted into the above equation to yield.
0.5•m•vi2 + m•g•hi = 0.5•m•vf2
By dividing each term of the equation by m, the mass can be canceled.
0.5 • vi2 + g • hi = 0.5 • vf2
Now known values can be substituted into this equation and the final velocity can be determined. The work is shown here:
0.5•(36.7 m/s)2 + (9.8 m/s/s)•(39.8 m) = 0.5 • vf2
673.4 m2/s2 + 390.0 m2/s2 = 0.5 • vf2
1063 m2/s2 = 0.5 • vf2
2127 m2/s2 = vf2
SQRT(2127 m2/s2) = vf
vf = 46.1 m/s
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
42. Claire deAisles has just completed her shopping at the grocery food store. She accidentally bumps her 42.5-kg cart, setting it in motion from rest down a hill inclined at 14.9 degrees. Upon descending a distance of 9.27 meters along the inclined plane, the cart hits a tree stump (which was placed in the parking lot for the sole purpose of this problem). A 0.295-kg can of tomato soup is immediately hurled from the moving cart and heads towards Will N. Tasue's brand new Lexus. Upon striking the Lexus, the tomato soup can creates a dent with a depth of 3.16 cm. Noah Formula, who is watching the entire incident and fixing to do some physics, attempts to calculate the average force which the Lexus applies to the soup can. Assume negligible air resistance and friction forces and help Noah out. PSYW
|
Answer: 218 N
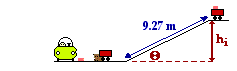 Here's an example of a physical situation in which gravity first acts to do work and convert the potential energy of a soup can (and the grocery cart) into kinetic energy; then a non-conservative force - the force of the Lexus applied to the soup can - serves to change the kinetic energy of the soup can. The problem is best analyzed if the cart itself is ignored and the focus becomes the soup can. The soup can begins with potential energy on top of the hill and finishes with no mechanical energy. The situation is depicted at the right. Here's an example of a physical situation in which gravity first acts to do work and convert the potential energy of a soup can (and the grocery cart) into kinetic energy; then a non-conservative force - the force of the Lexus applied to the soup can - serves to change the kinetic energy of the soup can. The problem is best analyzed if the cart itself is ignored and the focus becomes the soup can. The soup can begins with potential energy on top of the hill and finishes with no mechanical energy. The situation is depicted at the right.
The relevant equation becomes the work-energy equation:
KEi + PEi + Wnc = KEf + PEf
The final potential and kinetic energy can be canceled and the initial kinetic energy can be canceled (the can starts from rest).
PEi + Wnc = 0 J
The expressions for potential energy and work can be substituted into the above equation to derive:
m•g•hi + F•d•cos(theta) = 0 J
The initial height of the soup can is related to the angle of incline and the length along the incline according to the equation
sin(theta) = hi/L
The values of theta (14.9 degrees) and L (9.27 m) can be substituted into this equation and hi is found to be 2.38 m.
This hi value can be substituted into the work-energy equation along with the values of m (0.295 kg) and d (0.0316 m). The force can then be calculated. The work is shown here.
(0.295 kg)•(9.8 m/s/s)•(2.38 m) + F•(0.0316 m)•cos(180 deg) = 0 J
6.89 J - (0.0316m ) • F = 0 J
6.89 J = (0.0316m ) • F
F = 218 N
(Note there is an assumption in this problem that the collision with the Lexus chassis brings the soup can to a final rest position; This is likely not the case since a soup can typically does not become lodged inside the Lexus, but rather rebounds with a post-impact velocity. Yet without this assumption or further information, the problem cannot be solved.)
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
43. Pete Zaria applies a 11.9-Newton force to a 1.49-kg mug of root beer in order to accelerate it from rest over a distance of 1.42-m. Once released, how far will the mug slide along the counter top if the coefficient of friction is 0.728? PSYW
|
Answer: 0.170 m
Here is an instance in which there is only horizontal motion and a non-conservative force is doing work to change the kinetic energy of the mug. The entire motion will have to be divided into two parts - the part in which both friction and applied force act upon the mug (Pete is pushing it from position A to position B) and the part in which the mug is slowing down under the sole influence of friction (from position B to position C). The work-energy theorem (W = Delta KE) will be used to analyze each part.
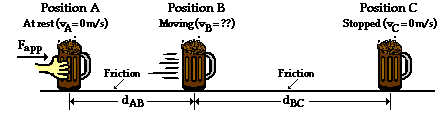
From position A to position B, Pete is pushing the mug and the net force upon the mug is simply the applied force minus the friction force (see free-body diagram below). From position B to position C, friction is the unbalanced force and acts as the net force (see free-body diagram below).
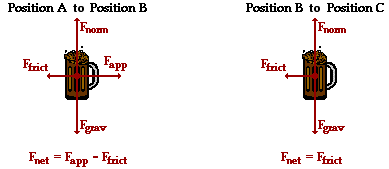
The force of friction is related to the normal force (= m•g) and the coefficient of friction (0.728). The Ffrict is
Ffrict = mu•Fnorm = (0.728) • (1.49 kg) • (9.8 m/s/s) = 10.6 N
This means that the net force from A to B is 11.9 N - 10.6 N = 1.27 N. The net force from B to C is 10.6 N.
From A to B, the work done equals the kinetic energy change. So the kinetic energy at position B is
KEB = W = F • d • cos(theta) = (1.27 N) • (1.42 m) • cos(0 deg) = 1.80 J
From B to C, the mug will lose this same amount of kinetic energy as friction works upon it to bring it to a stop. So the work done from B to C is -1.80 J.
W = Change in KE
F • d • cos(theta) = -1.80 J
(10.6 N) • (d) • cos(180 deg) = -1.80 J
- (10.6 N) • (d) = -1.80 J
d = 0.170 m
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
44. Suzie Lovtaski has a mass of 49.7 kg. She is at rest on top of a hill with a height of 92.6 m and an incline angle of 19.2 degrees. She coasts down the hill to the bottom and eventually comes to a stop; she never uses her poles to apply a force. The coefficient of friction is 0.0873 along the hill and 0.527 along the horizontal surface at the bottom. What total distance will Suzie coast (include both incline and level surface)? PSYW
|
Answer: 132 m
This problem is very similar to question #39 and can be treated in much the same way. There is a non-conservative force - friction - doing work upon the skier. This force will alter the total mechanical energy of the skier. The equation to be used is
KEi + PEi + Wnc = KEf + PEf
If we designate the level area at the bottom of the slope as the zero level of potential energy, then PEf is 0 J. Since Suzie eventually stops (due to the effect of friction along the level area), the KEf is 0 J. And since Suzie starts from rest, KEi = 0 J. So the above equation becomes
PEi + Wnc = 0
The Wnc term has two parts; there is friction doing along the inclined plane and friction doing work along the level surface. Since these two sections of the motion have different normal forces and friction coefficients (and therefore friction forces), they will have to be treated separately. The graphic below depicts the free-body diagrams and the means by which the friction force can be determined.

By substituting values of mu and mass and g and theta into the above equations, one finds that the friction values are
|
On Incline
Ffrict = 40.2 N
|
On Level Surface
Ffrict = 257 N
|
These forces act upon the skier over different distances. In the case of the inclined plane, the distance (d) can be computed from the given incline angle and the initial height. The relationship is depicted in the diagram below. The sine function is used to relate the angle to the initial height and the distance along the incline. In the case of the level surface, the distance is the unknown quantity (x) which this problem calls for.
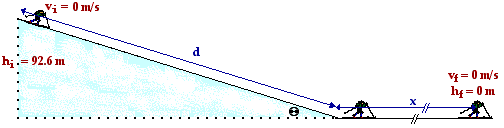
The distance d along the incline is
d = hi / sin(theta) = 92.6 m / sin(19.2 deg) = 282 m
Now substitutions can be made into the work-energy equation and algebraic manipulation can be performed to solve for x:
PEi + Wnc = 0
PEi + Wincline + Wlevel = 0
(49.7 kg)•(9.8 m/s)•(92.6 m) + (40.2 N)•(282 m)•cos(180 deg) + (257 N)•(x)•cos(180 deg) = 0 J
45102 J - 11307 J - 257 x = 0 J
33795 J = 257 x
132 m = x
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
45. Mia Kneezhirt jumps from a second story dorm room (h = 7.91 m) to the ground below. Upon contact with the ground, she allows her 62.4-kg body to come to an abrupt stop as her center of gravity is displaced downwards a distance of 89.2 cm. Calculate the average upward force exerted by the ground upon Mia's fragile body. PSYW
|
Answer: 5423 N
This is another instance of a non-conservative force (the force of the ground upon Mia's body) doing work in order to alter the total mechanical energy. The relevant equation is
KEi + PEi + Wnc = KEf + PEf
Since Mia starts from rest, the KEi term is 0 J and can be canceled. If we designate the ground to be the zero level, then the PEf term is 0 J and can be canceled as well. Since Mia is finally stopped by the upward applied force of the ground, the KEf term is 0 J and can be canceled. The original equation then simplifies to
PEi + Wnc = 0 J
Expressions for potential energy and work can be substituted into this equation to change its form to
m•g•hi + F•d•cos(theta) = 0 J
All quantities are known except for F, so values can be substituted into the equation and algebra can be used to solve for F. The work is shown here.
(62.4 kg) • (9.8 m/s/s) • (7.91 m) + F • (0.892 m) • cos(180 deg) = 0
4837 J - (0.892 m) • F = 0
4837 J = (0.892 m) • F
F = 5423 N
(Note that a critical assumption is made to make this problem solve-able. It is assumed that the Mia's center of mass starts a distance of 7.91 m above the position at which Mia's center of mass ultimately comes to rest. For most situations, this is usually a very safe assumption. In this case, the bending of Mia's knees would actually lower the center of gravity lower than the height that it would be at when she is just standing on the ground (in this case, 0.892 cm lower). Either this additional distance must be included in the PE term or it is assumed that Mia's landing involves somewhat of a spring action whereby she bends her knees to lower her body and then straightens up to an upright position - similar to the landing of an Olympic gymnast. The assumption is made in this problem that Mia utilizes the ground's force to not only stop her motion but to also elevate her back up to an upright position.)
|
[ #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 | #43 | #44 | #45 ]
Navigate to:
Review Session Home - Topic Listing
Work and Energy - Home || Printable Version || Questions with Links
Answers to Questions: All || #1-10 || #11-25 || #26-36 || #37-45
You Might Also Like ...
Users of The Review Session are often looking for learning resources that provide them with practice and review opportunities that include built-in feedback and instruction. If that is what you're looking for, then you might also like the following:
- The Calculator Pad
The Calculator Pad includes physics word problems organized by topic. Each problem is accompanied by a pop-up answer and an audio file that explains the details of how to approach and solve the problem. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to improve their problem-solving skills.
Visit: The Calculator Pad Home | Calculator Pad - Work and Energy
- Minds On Physics the App Series
Minds On Physics the App ("MOP the App") is a series of interactive questioning modules for the student that is serious about improving their conceptual understanding of physics. Each module of the series covers a different topic and is further broken down into sub-topics. A "MOP experience" will provide a learner with challenging questions, feedback, and question-specific help in the context of a game-like environment. It is available for phones, tablets, Chromebooks, and Macintosh computers. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to refine their conceptual reasoning abilities. Part 3 of the series includes topics in Work and Energy.
Visit: MOP the App Home || MOP the App - Part 3