About the Science Reasoning Center
 Highly Recommended
Highly RecommendedLike all our Science Reasoning Center activities, the completion of the Wave Speed activity requires that a student use provided information about a phenomenon, experiment, or data presentation to answer questions. This information is accessible by tapping on the small thumbnails found on the bottom right of every question. However, it may be considerably easier to have a printed copy of this information or to display the information in a separate browser window. You can access this information from this page.
The Standards
The Wave Speed activity focuses on the variables that affect the speed of a wave in a Slinky. Information about three short student experiments are presented to students. Students analyze the design of the experiment, identify appropriate claims and the supporting evidence for such claims, and use the patterns in the data to predict the result of subsequent trials. The activity includes a wide collection of questions that target the HS-PS4-1 performance expectation of the NGSS.
HS-PS4-1: Use mathematical representations to support a claimregarding relationships amongthe frequency, wavelength, and speed of waves traveling in various media.
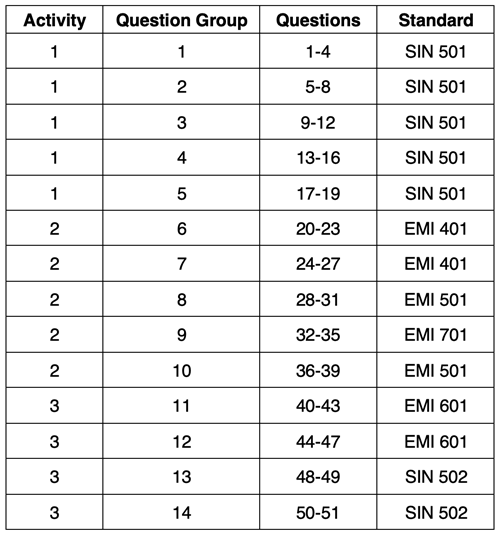
The activity consists of 51 questions organized into 14 Question Groups and spread across three activities. Success with the activity requires some degree of understanding or proficiency with respect to the following Disciplinary Core Idea, the Science and Engineering Practices, and the Crosscutting Concepts.
- Wave Properties: (Disciplinary Core Idea PS4.A):
The wavelength and frequency of a wave are related to one another by the speed of travel of the wave, which depends on the type of wave and the medium through which it is passing. - Asking Questions and Defining Problems (Science and Engineering Practice 1.1)
Ask questions that arise from careful observation of phenomena, or unexpected results, to clarify and/or seek additional information. - Developing and Using Models (Science and Engineering Practice 2.3)
Develop, revise, and/or use a model based on evidence to illustrate and/or predict the relationships between systems or between components of a system. - Planning and Carrying Out Investigations (Science and Engineering Practice 3.1)
Plan an investigation or test a design individually and collaboratively to produce data to serve as the basis for evidence as part of building and revising models, supporting explanations for phenomena, or testing solutions to problems. Consider possible variables or effects and evaluate the confounding investigation's design to ensure variables are controlled. - Analyzing and Interpreting Data(Science and Engineering Practice 4.1)
Analyze data using tools, technologies, and/or models (e.g., computational, mathematical) in order to make valid and reliable scientific claims or determine an optimal design solution. - Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking (Science and Engineering Practice 5.3)
Use mathematical, computational, and/or algorithmic representations of phenomena or design solutions to describe and/or support claims and/or explanations. - Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions (Science and Engineering Practice 6.1)
Make a quantitative and/or qualitative claim regarding the relationship between dependent and independent variables. - Patterns (Crosscutting Concept 1.2)
Empirical evidence is needed to identify patterns. - Cause and Effect (Crosscutting Concept 2.1)
Empirical evidence is required to differentiate between cause and correlation and make claims about specific causes and effects. - Scale, Proportion, and Quantity (Crosscutting Concept 3.2)
Algebraic thinking is used to examine scientific data and predict the effect of a change in one variable on another (e.g., linear growth vs. exponential growth). - Stability and Change (Crosscutting Concept 7.1)
Much of science deals with constructing explanations of how things change and how they remain stable.
While the Wave Speed activity stong NGSS alignment with the Disciplinary Core Idea, the six Science and Engineering Practices and the four Crosscutting Concepts above, the activity also drew inspiration from ACT's College Readiness Standards for Science Reasoning. Two strands (Scientific Investigation - SIN, and Evaluation of Models, Inferences, and Experimental Results - EMI) of the College Readiness Standards are addressed in this activity. The code given for the standard includes three letters to indicate the strand and three numbers to indicate the specific standard within that strand. Higher numbers are indicative of more complex science reasoning skills. The relationship between the questions and the standards is as follows:
Complementary and Similar Resources
The following resources at The Physics Classroom website complement the Wave Speed Science Reasoning Activity. Teachers may find them useful for supporting students and/or as components of lesson plans and unit plans.
Physics Classroom Tutorial, Vibrations and Waves: The Speed of a Wave
Physics Classroom Tutorial, Vibrations and Waves: The Wave Equation
Physics Video Tutorial, Vibrations and Waves: The Speed of a Wave
Physics Video Tutorial, Vibrations and Waves: Frequency-Wavelength-Speed Relationship
Physics Interactives, Waves and Sound: Simple Wave Simulation
Physics Interactives, Waves and Sound: Particle Wave Simulation
Concept Builders, Waves and Sound: Waves - Case Studies
Concept Builders, Waves and Sound: Wave Characteristics
Concept Builders, Waves and Sound: Rocking the Boat
Minds On Physics, Wave Motion Module, Mission WM3 - Speed of a Wave
Minds On Physics, Wave Motion Module, Mission WM4 - Wavelength, Frequency, Speed Relationships
The Calculator Pad, Vibrations and Waves: Problem Set WM5 - WM9
Recommended: Print Passage, Tables, and Graphs
Also see: