|
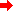
The diagram below depicts light reflecting off a planar surface. The incident and reflected rays are labeled. If ray A makes an angle of 25 degrees with the surface, then the angle of reflection is _____ degrees.
|
|
|
The Law of Reflection:
When a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The incident ray and reflected ray are always located within the same plane.
|

|
Definition of Angle of Incidence:
The angle of incidence is the angle made by the ray of light approaching a surface (incident ray) and the normal line drawn to the surface at the location where the ray contacts the surface.
Definition of Angle of Reflection:
The angle of reflection is the angle made by the ray of light leaving a surface (reflected ray) and the normal line drawn to the surface at the location where the ray leaves from the surface.
|
|

|
A common mistake made by beginning physics students is to believe that the angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the mirror surface. But don't be fooled! Angles of incidence (and reflection) are always measured between the ray of light and the normal line. If the angle between the incident ray and the mirror surface is 25 degrees, the angle of incidence is NOT 25 degrees. However, it can be determined using a quick math trick. See Math Magic section below.
|
|
|
The normal line makes a 90 degree angle with the mirror surface. The incident ray divides this 90 degree angle into two smaller angles - the angle of incidence and the angle between the mirror surface and the incident ray. The sum of these angle measures is equal to 90 degrees.
|
|
 What is the definition of the angle of incidence? What is the definition of the angle of incidence?
 What is the relationship between the angle measurements for an incoming light ray and an outgoing light ray? What is the relationship between the angle measurements for an incoming light ray and an outgoing light ray?
|