Hold down the T key for 3 seconds to activate the audio accessibility mode, at which point you can click the K key to pause and resume audio. Useful for the Check Your Understanding and See Answers.
Lesson 2: Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solutions
Part c: pH Indicators
Part a:
Water and its Ionization
Part b:
The pH Scale
Part c: pH Indicators
The Big Idea
Learn how pH indicators such as litmus, phenolphthalein, and bromothymol blue reveal the acidity or basicity of solutions by changing color at specific pH values.
What is a pH Indicator?
We have discussed a variety of everyday examples of acids and bases. And we have placed a variety of common solutions at locations along the pH scale. But exactly how does one know if a solution is an acid or a base and what its pH level is? After all, you can’t just go around safely tasting substances to see if they’re sour (acid) or bitter (base).
 Determination of the pH of solutions is commonly accomplished by using a pH indicator. A pH indicator is a substance that turns a particular color in a given pH range. A pH indicator can have the form of a solution or the form of a pH test strip. A couple drops of a pH indicator solution can be added to a solution of unknown pH. The indicator will turn a particular color based on the pH of that solution. A pH test strip is a strip of paper that is coated with a pH indicator. Dipping the strip into a solution and examining its color allows one to determine the relative pH range of the solution. Both pH indicators and pH test strips come with a pH color chart that relates an indicated color to a pH value or range of values. There are a variety of pH indicators available. We will discuss the most commonly used pH indicators.
Determination of the pH of solutions is commonly accomplished by using a pH indicator. A pH indicator is a substance that turns a particular color in a given pH range. A pH indicator can have the form of a solution or the form of a pH test strip. A couple drops of a pH indicator solution can be added to a solution of unknown pH. The indicator will turn a particular color based on the pH of that solution. A pH test strip is a strip of paper that is coated with a pH indicator. Dipping the strip into a solution and examining its color allows one to determine the relative pH range of the solution. Both pH indicators and pH test strips come with a pH color chart that relates an indicated color to a pH value or range of values. There are a variety of pH indicators available. We will discuss the most commonly used pH indicators.
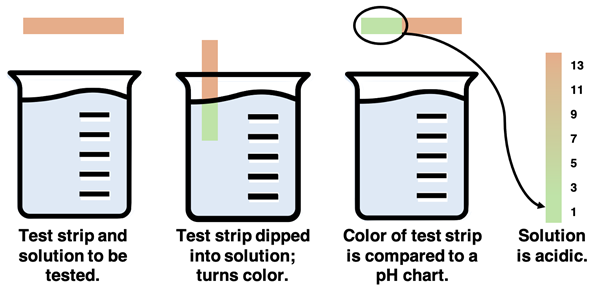
Litmus Paper as an Indicator
 Litmus paper is probably the most common indicator used in a Chemistry lab. The paper strip is coated with a pH indicator known as litmus. Litmus is a mixture of a variety of dyes that have been extracted from lichens (a collection of organisms found on rocks, trees, and soil). The paper strip turns red in acidic solutions and blue in basic solutions. By dipping the paper in a solution and observing its color, the solution can be classified as acidic or basic.
Litmus paper is probably the most common indicator used in a Chemistry lab. The paper strip is coated with a pH indicator known as litmus. Litmus is a mixture of a variety of dyes that have been extracted from lichens (a collection of organisms found on rocks, trees, and soil). The paper strip turns red in acidic solutions and blue in basic solutions. By dipping the paper in a solution and observing its color, the solution can be classified as acidic or basic.
Phenolphthalein Indicator
Phenolphthalein is another commonly used indicator in a chemistry lab. It is usually available as a solution. A couple of drops placed in a colorless solution will either turn pink to indicate a basic solution or remain colorless to indicate an acidic solution. The transition between colorless and pink occurs over a pH range between 8.2 and 10.0. Phenolphthalein (abbreviated as phth) is often used as an indicator in acid-base titration experiments.
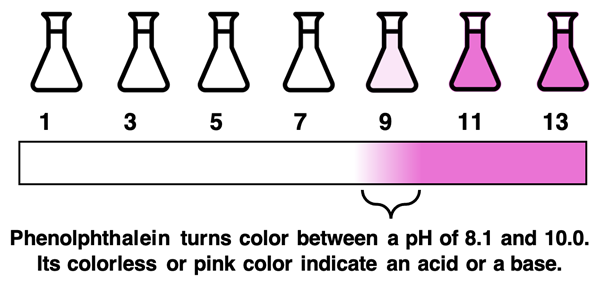
Other Acid-Base Indicators
There is a large number of acid-base indicators that can be used to determine the acidity or basicity of an acid or a base. Three other commonly used indicators are bromothymol blue, methyl red, and methyl orange. The graphic below illustrates their color in acidic and basic solutions and the pH range over which the color transition occurs.
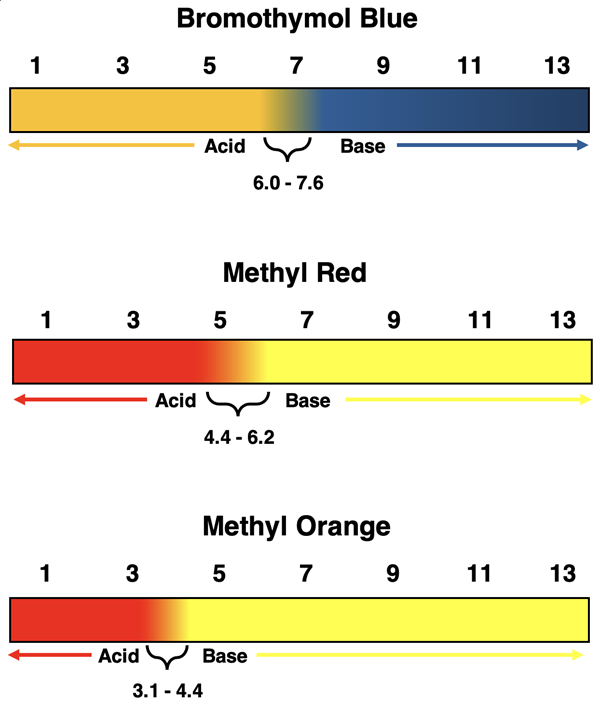
By performing two or more tests with carefully selected indicators, it is possible to narrow the pH for a solution as being within a narrow range. For instance, one might make these two observations of a solution of unknown pH:
- A test solution is colorless in the presence of phenolphthalein.
- A test solution turns yellow in the presence of methyl red.
What does this tell us about the pH value of the test solution? The first observation confirms that the pH is less than 8.1. The second observation confirms that the pH is greater than 6.2. Thus, the pH is somewhere in the range of 6.2 and 8.1.
Universal Indicator
A
universal indicator is not a single indicator. Rather, it is a mixture of many different indicators. The use of multiple indicators means that the solution will undergo multiple color changes across the entirety of the pH scale. As such, the use of a pH indicator allows one to make a more refined estimate of the pH of a solution. While a universal indicator provides considerably more specificity than a single pH indicator, it will still suggest a pH value that has an uncertainty as high as ±1 pH unit. The color chart below is a typical color chart for a universal indicator.
How Do Indicators Work?
An indicator is actually an acid that undergoes a reaction when in solution. Like any acid,
it donates a proton and becomes its conjugate base. It’s color as an acid is different than its color as a conjugate base. When a drop or two is added to a solution of unknown pH, it exists as a reversible system that can be shifted towards the acidic reactant or the conjugate base product. The
shift of the equilibrium position from one side to the other corresponds to a color change between its acid and its conjugate base color. The pH range at which the shifts occur vary from indicator to indicator.
Before You Leave - Practice and Reinforcement
Now that you've done the reading, take some time to strengthen your understanding and to put the ideas into practice. Here's some suggestions.
- Download our Study Card on pH Indicators. Save it to a safe location and use it as a review tool.
- The Check Your Understanding section below includes questions with answers and explanations. It provides a great chance to self-assess your understanding.
Check Your Understanding of pH Indicators
Use the following questions to assess your understanding of concepts associated with pH indicators. Tap the
Check Answer buttons when ready.
1. A pH indicator is unique in that ______.
- Its solubility is different in an acidic solution than in a basic solution.
- Its electrical conductivity is different in an acidic solution than in a basic solution.
- Its color is different in an acidic solution than in a basic solution.
- Its density is different in an acidic solution than in a basic solution.
2. Litmus turns red in ______.
- a neutral solution
- an acidic solution
- a basic solution
- any aqueous solution
3. An aqueous solution turns pink when phenolphthalein is added to it. Which of the following pH values might the solution have? Select all that apply.
- 4.0
- 7.0
- 7.5
- 10.5
- 14.0
4. A solution has a pH of 8.0. What color would it be in the presence of methyl orange?
- Orange
- Red
- Yellow
- Colorless
5. A solution has a pH of 3.0. What color would it be in the presence of methyl red?
- Orange
- Red
- Yellow
- Colorless
6. A solution with an unknown pH is a deep blue in the presence of bromothymol blue. The same solution will be ________ in the presence of phenolphthalein.
- Colorless
- Pink
- Gold
- Still Blue
7. Universal indicator is different than other simple indicators in that ______.
- It is only available as a pH test strip.
- It consists of an acid and its conjugate base.
- It has a single pH value at which it changes color.
- It changes different colors at several different pH values.

8. A scientific supply house provides the pH Color Chart shown at the right with their universal indicator. Which two of the following statements are correct?
- Acidic solutions will display red, orange, and yellow colors when a couple of drops of the indicator are added.
- Acidic solutions will display blue, violet, and purple colors when a couple of drops of the indicator are added.
- Basic solutions will display red, orange, and yellow colors when a couple of drops of the indicator are added.
- Basic solutions will display blue, violet, and purple colors when a couple of drops of the indicator are added.
9. Universal indicator is preferred over other indicators because ______.
- It is less toxic.
- It is less expensive
- It has a radically cool range of colors.
- It is more capable of determining a specific pH value.